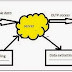
There are 4 types of Properties to Identify the Objects in QTP
1) Mandatory properties
2) Assistive properties
3) Ordinal Identifier
Mandatory properties: Mandatory properties are properties that QuickTest always learns for a particular test object class.
Assistive properties are properties that QuickTest learns only if the mandatory properties that QuickTest learns for a particular object in your application are not sufficient to create a unique description. If several assistive properties are defined for an object class, then QuickTest learns one assistive property at a time and stops as soon as it creates a unique description for the object. If QuickTest does learn assistive properties, those properties are added to the test object description.
If the combination of all defined mandatory and assistive properties is not sufficient to create a unique test object description, QuickTest also records the value for the selected ordinal identifier.
Ordinal Identifier:
In general, there are two types of ordinal identifiers:
Index—indicates the order in which the object appears in the application code relative to other objects with an otherwise identical description.
Location—indicates the order in which the object appears within the parent window, frame, or dialog box relative to other objects with an otherwise identical description. Values are assigned from top to bottom, and then left to right.
The Web Browser object has a third ordinal identifier type:
If the combination of all defined mandatory and assistive properties is not sufficient to create a unique test object description, QuickTest also records the value for the selected ordinal identifier.
Ordinal Identifier:
In general, there are two types of ordinal identifiers:
Index—indicates the order in which the object appears in the application code relative to other objects with an otherwise identical description.
Location—indicates the order in which the object appears within the parent window, frame, or dialog box relative to other objects with an otherwise identical description. Values are assigned from top to bottom, and then left to right.
The Web Browser object has a third ordinal identifier type:
CreationTime—indicates the order in which the browser was opened relative to other open browsers with an otherwise identical description. Each test object class has a default ordinal identifier selected.

Configuring Mandatory properties
In object identification dialog box select the object class from test object classes list and go to Mandatory properties for that class.
Click on Add/Remove button and select or deselect the properties you want to configure.
Configuring Assistive Properties
In object identification dialog box select the object class from test object classes list and go to Assistive properties for that class.
Click on Add/Remove button and select or deselect the properties you want to configure.
Configuring Ordinal Identifiers
To modify the selected ordinal identifier, select the desired type from the Ordinal identifier box.
Smart Identification:Configuring Mandatory properties
In object identification dialog box select the object class from test object classes list and go to Mandatory properties for that class.
Click on Add/Remove button and select or deselect the properties you want to configure.
Configuring Assistive Properties
In object identification dialog box select the object class from test object classes list and go to Assistive properties for that class.
Click on Add/Remove button and select or deselect the properties you want to configure.
Configuring Ordinal Identifiers
To modify the selected ordinal identifier, select the desired type from the Ordinal identifier box.
When QuickTest uses the recorded description to identify an object, it searches for an object that matches every one of the property values in the description. In most cases, this description is the simplest way to identify the object and unless the main properties of the object change, this method will work.
If QuickTest is unable to find any object that matches the recorded object description, or if it finds more than one object that fits the description, then QuickTest ignores the recorded description, and uses the Smart Identification mechanism to try to identify the object.