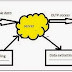
Set (Interface)
1) Set is an un-ordered collection which doesn’t allows duplicate (no-duplicate) elements
2) We can iterate the values by calling iterator() method
List (Interface)
1) List is an ordered collection which allows duplicate elements
2) We can iterate the values by calling iterator() method
Map (Interface)
1) In Map we used to store the data in key and value pairs, we may have duplicate values but no duplicate keys
2) In Map we don’t have iterator() method, but we can get the keys by calling the method keySet()
Map m; // insert values
Set s = m.keySet();
// Get Map keys into the Set and then iterate this Set object normally
// m.keySet() returns Set object with Map keys
Iterator iter = s.iterator();
Follow @TestingQ
1) Set is an un-ordered collection which doesn’t allows duplicate (no-duplicate) elements
2) We can iterate the values by calling iterator() method
Set s = new HashSet();
Iterator iter = s.iterator();
Iterator iter = s.iterator();
List (Interface)
1) List is an ordered collection which allows duplicate elements
2) We can iterate the values by calling iterator() method
List li = new ArrayList();
Iterator iter = li.iterator();
Iterator iter = li.iterator();
Map (Interface)
1) In Map we used to store the data in key and value pairs, we may have duplicate values but no duplicate keys
2) In Map we don’t have iterator() method, but we can get the keys by calling the method keySet()
Map m; // insert values
Set s = m.keySet();
// Get Map keys into the Set and then iterate this Set object normally
// m.keySet() returns Set object with Map keys
Iterator iter = s.iterator();